background
material
 selection selection
 recording recording
 gating gating
responses
download
paper preprint
contact
DCS project
|
The phonemic vowel
and consonant inventory used for the diphone selection was based on
the Dutch CELEX lexical
database and on "The phonology of Dutch" by Booij (Oxford: Oxford University
Press, 1995). Not all possible phonemes were used, however. Reasons
for the selection or exclusion of particular phonemes were the following:
-
Besides the voiceless velar fricativ /x/, CELEX recognizes the voiced velar
fricativ /
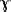 /. The phoneme was
excluded because many Dutch speakers neutralize the distinction, maintaining
only / /. The phoneme was
excluded because many Dutch speakers neutralize the distinction, maintaining
only / 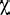 /. /.
-
The vowels /
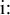 , , 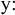 , , 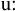 , , 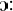 , , 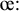 , , 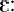 / occur only in unassimilated loanwords (such as "analyse, centrifuge,
cruise, oeuvre, serre" respectively) and differ from native vowels phonemes
only in length. These vowels were excluded because they only occur in a
small number of recent loanwords.
/ occur only in unassimilated loanwords (such as "analyse, centrifuge,
cruise, oeuvre, serre" respectively) and differ from native vowels phonemes
only in length. These vowels were excluded because they only occur in a
small number of recent loanwords.
-
Nevertheless a number of consonants which occur in Dutch only in unassimilated
loanwords were included, such as the voiced velar stop /g/, the fricative
/
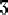 /, and the affricate / /, and the affricate / 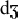 /, since they appear in a relatively large number of loanwords, many of
them quite frequent (e.g. "goal", "jam", and "jazz").
/, since they appear in a relatively large number of loanwords, many of
them quite frequent (e.g. "goal", "jam", and "jazz").
-
There are certain inconsistencies in the CELEX inventory, such as the fact
that [
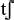 ] is treated as a sequenceof a
stop and a fricative, / ] is treated as a sequenceof a
stop and a fricative, /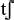 /, while [ /, while [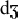 ]
is treated as a single affricate segment / ]
is treated as a single affricate segment /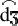 /. In these cases it has been adhered to the CELEX standard.
/. In these cases it has been adhered to the CELEX standard.
For the combination of phonemes into diphones the following general
rules were applied:
-
For each sequence of two phonemes containing a vowel other than /
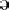 / (which is never stressed), one diphone was included with the vowel stressed,
and another with it unstressed. For vowel-vowel diphones, all four stress
combinations (stressed-stressed, unstressed- unstressed, stressed-unstressed,
unstressed-stresses) were included.
/ (which is never stressed), one diphone was included with the vowel stressed,
and another with it unstressed. For vowel-vowel diphones, all four stress
combinations (stressed-stressed, unstressed- unstressed, stressed-unstressed,
unstressed-stresses) were included.
-
Diphones which can only occur across word or morpheme boundaries in Dutch
were included (e.g. /
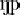 /), whereas
such diphones were excluded which could never occur even across word boundaries,
because of phonotactic constraints. /), whereas
such diphones were excluded which could never occur even across word boundaries,
because of phonotactic constraints.
-
In cases where phonotactic constraints were violated by large numbers of
loanwords the diphone were included.
-
Excluded were certain diphones which are possible (at least across morpheme
boundaries) according to a phoneme transcription, but unlikely ever to
be produced as a sequence of the two sounds (e.g., /
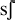 , , 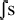 , , 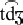 /).
/).
-
All sequences of identical consonants were excluded, since Dutch phonology
requires that these be degeminated within the prosodic word, and they are
likely to be reduced to a singel consonant even across word boundaries
unless produced with a pause.
-
A few diphones which probably never occur in Dutch, e.g. /
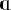 , , 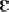 , , 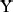 / followed by /
/ followed by / 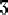 /, were included
simply because no known phonotactic constraint excludes them. /, were included
simply because no known phonotactic constraint excludes them.
The table below gives a full list of rules defining our final set
of diphones.
CV diphones |
C |
V |
stop, affricate, nasal, liquid,
or glide |
p, t, k, b, d, g, 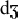 , m, n, , m, n, 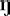 ,
r, l, j, w ,
r, l, j, w |
all full vowels stressed,
all vowels unstressed |
| fricative |
f, v, s, z, 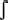 , , 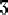 ,
x, h ,
x, h |
all full vowels stressed |
f, v, s, z, 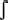 , , 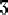 ,
x ,
x |
all vowels unstressed |
| h |
all full vowels unstressed |
Exclusion:
/ 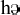 / within the syllable, and
/h/ cannot be syllable-final / within the syllable, and
/h/ cannot be syllable-final
|
VC diphones |
V |
C |
| stop, affricate, liquid, or glide |
all full vowels stressed,
all vowels unstressed |
p, t, k, b, d, g, 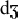 , r, l,
j, w , r, l,
j, w |
| fricative |
all full vowels stressed,
all vowels unstressed |
f, s, 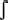 , , 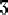 ,
r, l, j, w ,
r, l, j, w |
all long vowels and diphthongs stressed;
all long vowels, diphthongs, and / 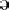 / unstressed
/ unstressed |
v, z |
Exclusion:
short vowel before /v, z/ is not possible within the syllable, and short
vowels cannot be syllable-final
|
| nasal |
all full vowels stressed |
m, n |
all short vowels stressed; all short vowels and / 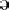 / unstressed
/ unstressed |
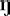 |
Exclusion:
/ 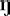 / cannot follow long vowels within
the syllable and cannot be syllable-initial / cannot follow long vowels within
the syllable and cannot be syllable-initial
|
VV diphones |
V1 |
V2 |
| stressed-unstressed |
all long vowels & diphthongs |
all vowels |
| unstressed-stressed |
all long vowels, diphthongs, & 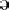
|
all vowels except 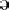 |
| unstressed-unstressed |
all long vowels, diphthongs, & 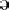
|
all vowels |
| stressed-stressed |
all long vowels & diphthongs |
all vowels except 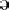 |
 |
Exclusion for
all VV categories: short vowel cannot be V1 because
they cannot be syllable-final
|
CC diphones |
C |
C |
| voiceless stop, nasal, liquid, or glide |
p, t, k, m, n, 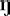 , l, r, j, w , l, r, j, w |
all consonants except C1=C2
and / 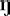 / / |
Exclusion:
/ 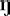 / cannot follow a stop or another
sonorant within the syllable or be an onset / cannot follow a stop or another
sonorant within the syllable or be an onset
|
| voiced stop |
b |
d, g, 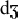 , v, z, , v, z, 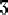 ,
n, l, r ,
n, l, r |
| d |
b, g, v, z, 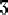 , n, j, w , n, j, w |
Exclusion for
/b, d/: /bw, bj, bm, dl/ in syllable onset, and voiced stops must devoice
if not on onset unless followed by a voiced obstruent; cannot be followed
by / 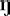 / because / / because / 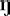 / cannot be an onset
/ cannot be an onset
|
| g |
b, d, v, z |
Exclusions:
syllable-final /g/ without devoicing is only followed by these consonants,
and /g/ is never word-final
|
| fricative |
f |
all consonants except f, v, 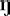 |
Exclusion:
/fv/ is too difficult for speakers to produce without assimilation
|
s, 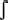 |
all consonants except s, 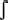 , , 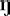 |
Exclusion:
/ 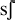 / and / / and / 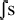 / are unlikely, unless assimilated
/ are unlikely, unless assimilated |
| x |
all consonants except x, 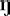 |
| v |
b, d, g, z, 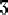 , , 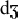 ,
n, l, r ,
n, l, r |
Exclusion:
/vj, vw, vm/ as onsets and /v/ must devoice if not in onset
|
| z |
b, d, g, v, 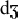 , m, n, j, w , m, n, j, w |
Exclusion:
/zl, zr/ as onsets and /z/ must devoice if not on onset; / 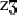 / is likely to assimilate
/ is likely to assimilate |
Exclusions for /v, z/: cannot
be followed by a voiceless fricative within the syllable, and will devoice
in coda position unless followed by a voiced obstruent
|
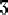 |
w |
Exclusions:
/ 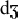 / never occurs syllable-finally
and in onset occurs only before vowels or /w/ (e.g. "bourgeois") / never occurs syllable-finally
and in onset occurs only before vowels or /w/ (e.g. "bourgeois") |
Exclusions for all fricative:
/ 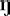 / cannot follow a fricative within
the syllable and cannot be an onset / cannot follow a fricative within
the syllable and cannot be an onset
|
| affricate |
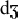 |
m |
Exclusions:
/ 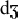 / never occurs word-finally,
occurs syllable-finally only in the word "management", and cannot be followed
by any other consonant within an onset / never occurs word-finally,
occurs syllable-finally only in the word "management", and cannot be followed
by any other consonant within an onset |
Exclusions for all CC diphones:
no geminates
|
Many of the diphones were recorded in several stress conditions.
Stress for consonant C (i.e., the syllable
the consonant was part of) was chosen as follows (the dash symbol indicates
syllable boundary):
-
CV: one syllable, stressed or unstressed
-
C1C2: one stressed syllable,
or
-
C1-C2: two syllables with stress
on the first
-
V-C: two syllables with either stress on first or on second syllable
Stress for consonant V was chosen as follows:
-
CV: one syllable, stressed or unstressed
-
V-C: two syllables with either stress on first or on second syllable
-
V1-V2: two syllables with stress
on first or second or both or neither.
 |
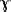 /. The phoneme was
excluded because many Dutch speakers neutralize the distinction, maintaining
only /
/. The phoneme was
excluded because many Dutch speakers neutralize the distinction, maintaining
only / 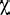 /.
/. 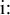 ,
, 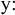 ,
, 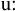 ,
, 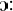 ,
, 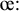 ,
, 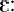 / occur only in unassimilated loanwords (such as "analyse, centrifuge,
cruise, oeuvre, serre" respectively) and differ from native vowels phonemes
only in length. These vowels were excluded because they only occur in a
small number of recent loanwords.
/ occur only in unassimilated loanwords (such as "analyse, centrifuge,
cruise, oeuvre, serre" respectively) and differ from native vowels phonemes
only in length. These vowels were excluded because they only occur in a
small number of recent loanwords. 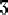 /, and the affricate /
/, and the affricate / 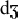 /, since they appear in a relatively large number of loanwords, many of
them quite frequent (e.g. "goal", "jam", and "jazz").
/, since they appear in a relatively large number of loanwords, many of
them quite frequent (e.g. "goal", "jam", and "jazz"). 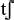 ] is treated as a sequenceof a
stop and a fricative, /
] is treated as a sequenceof a
stop and a fricative, /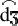 /. In these cases it has been adhered to the CELEX standard.
/. In these cases it has been adhered to the CELEX standard. 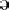 / (which is never stressed), one diphone was included with the vowel stressed,
and another with it unstressed. For vowel-vowel diphones, all four stress
combinations (stressed-stressed, unstressed- unstressed, stressed-unstressed,
unstressed-stresses) were included.
/ (which is never stressed), one diphone was included with the vowel stressed,
and another with it unstressed. For vowel-vowel diphones, all four stress
combinations (stressed-stressed, unstressed- unstressed, stressed-unstressed,
unstressed-stresses) were included. 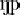 /), whereas
such diphones were excluded which could never occur even across word boundaries,
because of phonotactic constraints.
/), whereas
such diphones were excluded which could never occur even across word boundaries,
because of phonotactic constraints. 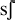 ,
, 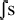 ,
, 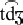 /).
/). 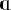 ,
, 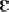 ,
, 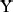 / followed by /
/ followed by / 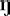 ,
r, l, j, w
,
r, l, j, w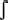 ,
, 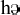 / within the syllable, and
/h/ cannot be syllable-final
/ within the syllable, and
/h/ cannot be syllable-final
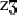 / is likely to assimilate
/ is likely to assimilate